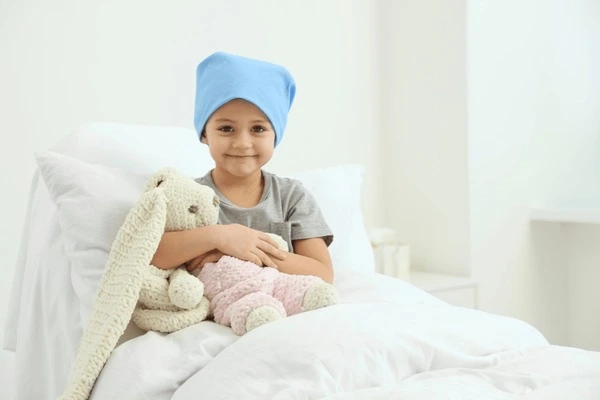
Services

Pediatric Oncology
Pediatric oncology physicians are specially trained to care for children, ensuring their comfort and well-being throughout the treatment process.

Solid Tumors
Tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and solid tumors may form anywhere.

Brain Tumor
Brain tumors are the second most common childhood cancer, with symptoms like headaches, nausea, and seizures.
Bone Tumors
Bone tumors form from uncontrolled cell growth in bones, causing pain, tenderness, and limited mobility.

Kidney or Liver Tumour
Kidney, adrenal, and liver tumors may be cancerous, treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, or transplantation.

Muscle Tumour
Muscle tumors, or soft tissue sarcomas, may require surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and rehabilitation for treatment.

Histiocytic Disorder
Histiocytic disorders involve excess histiocytes causing tissue damage; treatment may include chemotherapy, stem cell transplantation, and immunotherapy.



